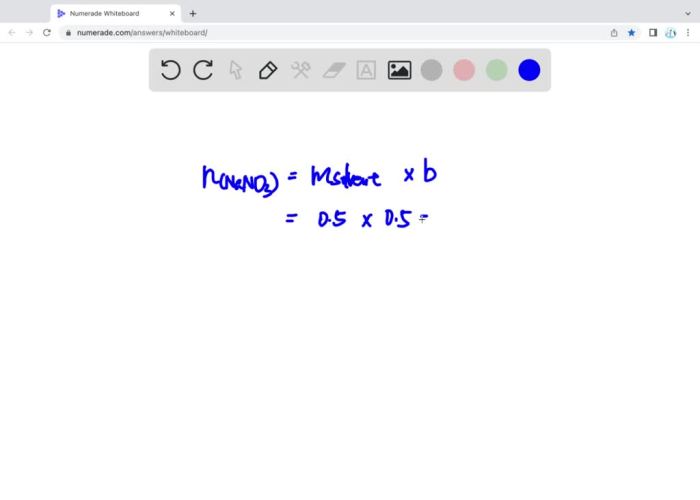
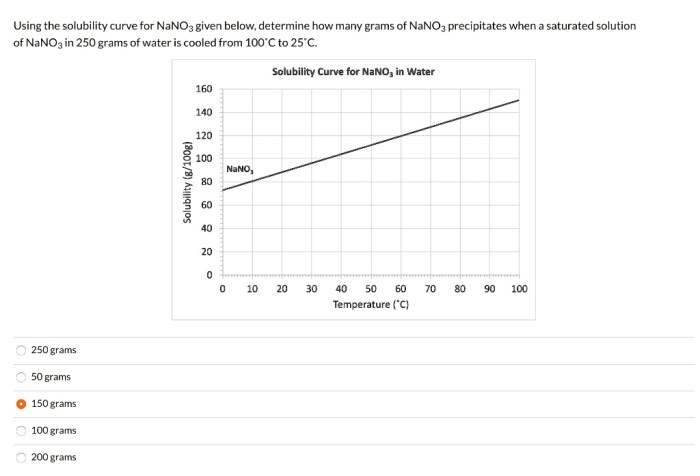
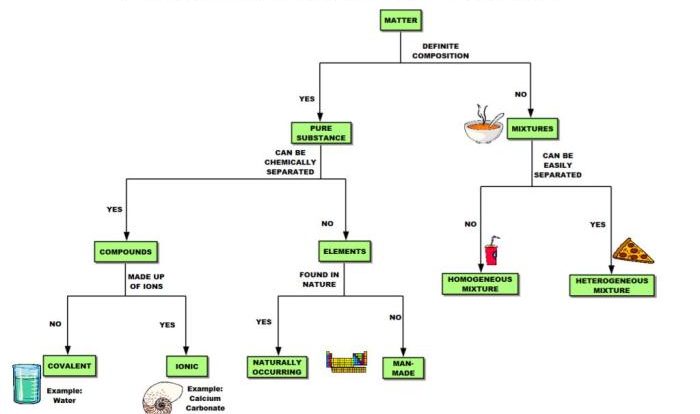
A solution that contains 70g of nano3 at 30 c – A solution containing 70g of NaNO3 at 30°C presents a captivating subject for scientific inquiry, offering insights into the fundamental principles of solution chemistry. This in-depth exploration delves into the concepts of solution concentration, molarity, temperature, solubility, and colligative properties, providing a comprehensive understanding of the behavior of solutes in solution.
Beyond theoretical foundations, this analysis also examines the practical applications of solutions in various fields, including industry, medicine, and agriculture. By unraveling the intricacies of solution chemistry, we gain a deeper appreciation for its significance in shaping our understanding of the world around us.
Solution Concentration: A Solution That Contains 70g Of Nano3 At 30 C

Solution concentration is a measure of the amount of solute dissolved in a given amount of solvent. The most common units of concentration are molarity (M), molality (m), and percent by mass (% m/m). Molarity is defined as the number of moles of solute per liter of solution, molality is defined as the number of moles of solute per kilogram of solvent, and percent by mass is defined as the mass of solute per 100 grams of solution.
To calculate the concentration of a solution, you need to know the mass of the solute and the volume of the solution. Once you have this information, you can use the following formula to calculate the concentration:
“`Concentration = (Mass of solute / Molecular weight of solute) / Volume of solution“`
Molarity
Molarity is the most commonly used unit of concentration. It is defined as the number of moles of solute per liter of solution. To calculate the molarity of a solution, you need to know the number of moles of solute and the volume of the solution in liters.
Once you have this information, you can use the following formula to calculate the molarity:
“`Molarity = Number of moles of solute / Volume of solution (in liters)“`
Molarity is a useful unit of concentration because it allows you to easily compare the concentrations of different solutions. For example, a solution with a molarity of 1 M has the same number of moles of solute per liter of solution as a solution with a molarity of 1 M, regardless of the solvent used.
Temperature and Solubility
The solubility of a solute is the maximum amount of solute that can be dissolved in a given amount of solvent at a given temperature. The solubility of a solute is affected by several factors, including the temperature of the solvent and the nature of the solute and solvent.
The solubility of a solute generally increases with increasing temperature. This is because the higher the temperature, the more energy the solvent molecules have, and the more likely they are to break apart the solute molecules and dissolve them.
Colligative Properties
Colligative properties are properties of solutions that depend on the concentration of the solute, but not on the nature of the solute. Colligative properties include boiling point elevation, freezing point depression, osmotic pressure, and vapor pressure lowering.
The boiling point elevation of a solution is the difference between the boiling point of the pure solvent and the boiling point of the solution. The boiling point elevation of a solution is directly proportional to the concentration of the solute.
Chemical Reactions in Solution
Chemical reactions can occur in solution just as they can in the gas phase or the liquid phase. When a chemical reaction occurs in solution, the reactants and products are dissolved in a solvent. The solvent does not participate in the reaction, but it can affect the rate of the reaction.
The rate of a chemical reaction in solution is affected by several factors, including the concentration of the reactants, the temperature of the solution, and the presence of a catalyst.
Applications of Solutions, A solution that contains 70g of nano3 at 30 c
Solutions are used in a wide variety of applications in everyday life. Some of the most common applications of solutions include:
- Cleaning
- Cooking
- Medicine
- Agriculture
- Industry
Quick FAQs
What is the molarity of a solution containing 70g of NaNO3 in 1 liter of solution?
To calculate molarity, we use the formula: Molarity = moles of solute / volume of solution in liters. First, we convert the mass of NaNO3 to moles: 70g / 85 g/mol = 0.824 moles. Then, we divide the moles by the volume of the solution: 0.824 moles / 1 liter = 0.824 M.
How does temperature affect the solubility of NaNO3?
Temperature has a positive effect on the solubility of NaNO3. As temperature increases, the kinetic energy of the solvent molecules increases, which allows them to break apart the solute particles more effectively, leading to increased solubility.
What are the colligative properties of a solution containing NaNO3?
Colligative properties are properties that depend on the concentration of the solute particles in a solution, regardless of the nature of the solute. The colligative properties of a solution containing NaNO3 include boiling point elevation, freezing point depression, vapor pressure lowering, and osmotic pressure.