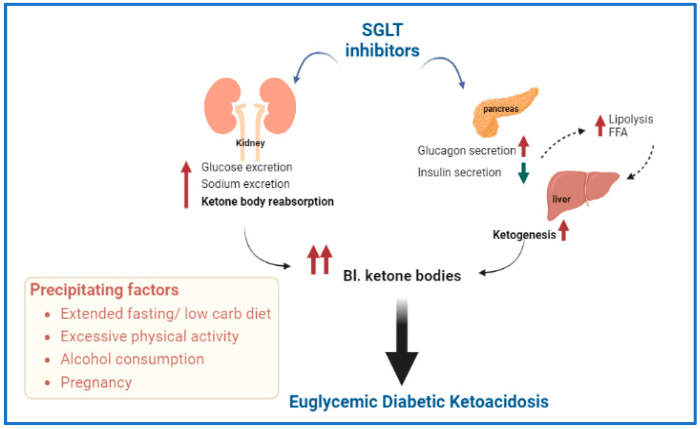
As diabetic people’s bodies are less efficient at clearing substances, a multitude of health concerns arise. This article delves into the causes, consequences, and management strategies associated with this reduced efficiency, shedding light on the complexities of diabetes and its impact on the human body.
Delving into the intricacies of diabetic physiology, we uncover the factors that contribute to this impaired clearance, including insulin resistance and disrupted glucose metabolism. The consequences of this reduced efficiency extend beyond short-term complications, potentially leading to severe long-term health issues such as cardiovascular disease, stroke, and kidney failure.
Diabetic People’s Bodies: Diabetic People’s Bodies Are Less Efficient At Clearing
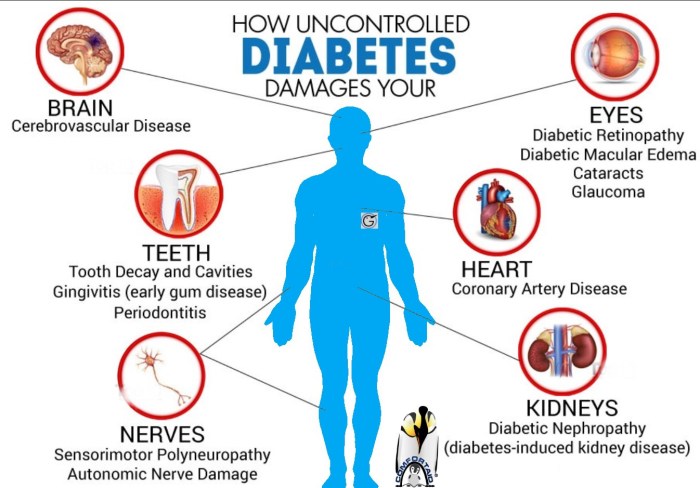
Diabetic people’s bodies are less efficient at clearing glucose from the blood. This is because their bodies do not produce enough insulin or do not use insulin properly. Insulin is a hormone that helps glucose get from the blood into cells, where it can be used for energy.
When glucose cannot get into cells, it builds up in the blood. High blood glucose levels can damage blood vessels and nerves, and can lead to serious health problems, such as heart disease, stroke, kidney failure, and blindness.
Causes of Reduced Efficiency
The following factors can contribute to reduced efficiency in diabetic people’s bodies:
- Insulin resistance: This is a condition in which the body’s cells do not respond to insulin properly. As a result, glucose cannot get into cells and builds up in the blood.
- Impaired glucose metabolism: This is a condition in which the body does not produce enough insulin or does not use insulin properly. As a result, glucose cannot get into cells and builds up in the blood.
Consequences of Reduced Efficiency
Reduced efficiency in diabetic people’s bodies can have the following short-term and long-term consequences:
- Short-term consequences: High blood glucose levels can cause symptoms such as thirst, frequent urination, fatigue, and blurred vision.
- Long-term consequences: High blood glucose levels can damage blood vessels and nerves, and can lead to serious health problems, such as heart disease, stroke, kidney failure, and blindness.
Management Strategies
The following strategies can be used to manage reduced efficiency in diabetic people’s bodies:
- Lifestyle modifications: These include eating a healthy diet, getting regular exercise, and maintaining a healthy weight.
- Medications: These include insulin and other medications that can help lower blood glucose levels.
- Therapies: These include insulin pump therapy and continuous glucose monitoring.
Research and Advancements, Diabetic people’s bodies are less efficient at clearing
There is ongoing research to better understand and improve efficiency in diabetic people’s bodies. This research includes:
- Developing new medications and therapies to help lower blood glucose levels.
- Studying the role of genetics and environmental factors in the development of diabetes.
- Developing new technologies to help people with diabetes manage their condition.
Top FAQs
What factors contribute to reduced efficiency in diabetic bodies?
Insulin resistance and impaired glucose metabolism are key factors that disrupt the body’s ability to effectively clear substances.
How can reduced efficiency impact long-term health?
Over time, reduced efficiency can increase the risk of severe complications, including heart disease, stroke, and kidney failure.
What management strategies are available for reduced efficiency in diabetic individuals?
Lifestyle modifications, such as exercise and dietary changes, along with medications and therapies, can help improve efficiency and mitigate the risks associated with diabetes.