The Dew Point and Relative Humidity Worksheet provides a comprehensive exploration of these critical weather parameters. It delves into their definitions, calculations, and implications in various fields, offering a thorough understanding of their significance in weather forecasting, building science, human comfort, and industrial processes.
This worksheet is an invaluable resource for students, professionals, and anyone seeking to enhance their knowledge of dew point and relative humidity.
Definition of Dew Point and Relative Humidity: Dew Point And Relative Humidity Worksheet
Dew point is the temperature at which air becomes saturated with water vapor and condensation begins to form. It is a crucial parameter in weather forecasting as it indicates the potential for precipitation and cloud formation.
Relative humidity (RH) is the ratio of the actual water vapor content in the air to the maximum amount of water vapor that the air can hold at a given temperature. It is expressed as a percentage and indicates the moisture level in the air.
Calculating Dew Point and Relative Humidity
Dew point can be calculated using the following formula:
Tdp= T
- (100
- RH) / 5
where:
- T dpis the dew point in degrees Celsius
- T is the air temperature in degrees Celsius
- RH is the relative humidity in percentage
Relative humidity can be calculated using the following formula:
RH = (e / es) x 100%
where:
- RH is the relative humidity in percentage
- e is the actual water vapor pressure in millibars
- e sis the saturation water vapor pressure in millibars
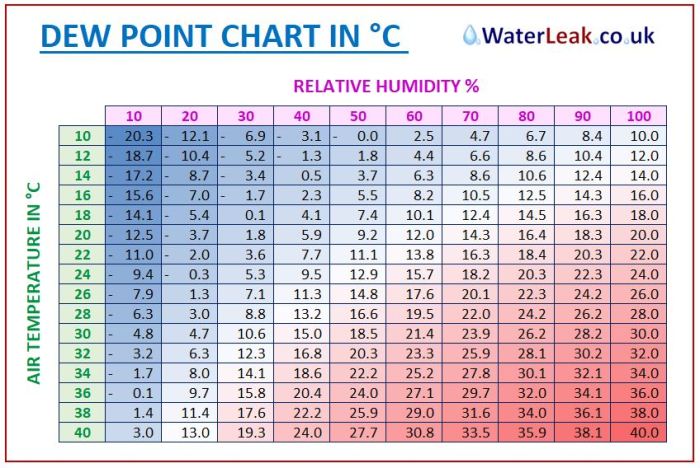
Psychrometric charts can also be used to determine dew point and relative humidity based on air temperature and wet-bulb temperature.
Factors Affecting Dew Point and Relative Humidity
Dew point and relative humidity are primarily influenced by temperature and moisture content in the air.
- As temperature increases, the air’s capacity to hold water vapor increases, resulting in lower relative humidity.
- As moisture content increases, the dew point and relative humidity both increase.
Additionally, dew point and relative humidity can vary with altitude and weather conditions. At higher altitudes, the air is less dense and can hold less water vapor, leading to lower dew points and relative humidity.
Dew Point and Relative Humidity in Weather Forecasting
Dew point and relative humidity play a crucial role in predicting precipitation. When the dew point is close to the air temperature, the air is nearly saturated with water vapor, increasing the likelihood of cloud formation and precipitation.
Dew point spread, the difference between the dew point and the air temperature, is used to assess atmospheric stability. A small dew point spread indicates stable air, while a large dew point spread indicates unstable air, which is more conducive to cloud formation and precipitation.
Dew Point and Relative Humidity in Building Science, Dew point and relative humidity worksheet
Dew point and relative humidity are important considerations in building design and construction. When the dew point exceeds the surface temperature, condensation can occur, leading to moisture problems and structural damage.
To prevent condensation, it is crucial to maintain a low dew point in indoor spaces. This can be achieved through proper ventilation, insulation, and vapor barriers.
Dew Point and Relative Humidity in Human Comfort
Dew point and relative humidity significantly impact human thermal comfort. High dew point and relative humidity levels can lead to discomfort, as the body struggles to evaporate sweat and cool down.
Optimal thermal comfort is achieved when the dew point is between 9-12°C (48-54°F) and the relative humidity is between 40-60%.
Dew Point and Relative Humidity in Industrial Processes
Dew point and relative humidity are critical factors in various industrial processes, including manufacturing, food processing, and pharmaceuticals.
- In manufacturing, high dew point can lead to corrosion and damage to equipment and products.
- In food processing, low dew point is crucial to prevent food spoilage and ensure product quality.
- In pharmaceuticals, controlled dew point and relative humidity are essential for maintaining the stability and efficacy of drugs.
Key Questions Answered
What is the difference between dew point and relative humidity?
Dew point is the temperature at which water vapor in the air condenses into liquid water, while relative humidity is a measure of the amount of water vapor in the air compared to the maximum amount it can hold at a given temperature.
How can I calculate dew point?
You can use the following formula: Dew Point = (243.04 – ln(RH/100) + 17.625 – T) / (17.625 – ln(RH/100)), where RH is the relative humidity in % and T is the air temperature in °C.
How does dew point affect human comfort?
High dew points can make the air feel muggy and uncomfortable, especially when combined with high temperatures. This is because the body cannot evaporate sweat as effectively when the dew point is high.