The Kinetic Energy Worksheet with Answers is an invaluable resource for students and educators seeking to delve into the fascinating realm of kinetic energy. This comprehensive guide unravels the intricate concept of kinetic energy, providing a clear understanding of its formula and applications in real-world scenarios.
The worksheet presents a series of problems that gradually increase in complexity, challenging students to apply their understanding of kinetic energy. Each problem is meticulously solved, revealing the step-by-step process involved in calculating kinetic energy. The accompanying answer key further reinforces students’ comprehension, ensuring their mastery of the subject.
Introduction
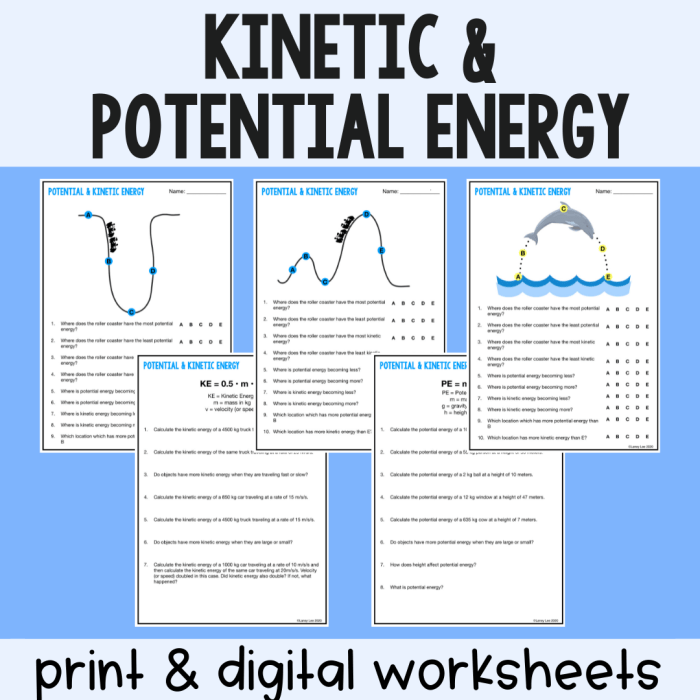
Kinetic energy is the energy of motion. It is defined as the work needed to accelerate a body of mass (m) from rest to velocity (v). The formula for calculating kinetic energy is:
$$K = 1/2
- m
- v^2$$
Where:
- K is kinetic energy in joules (J)
- m is mass in kilograms (kg)
- v is velocity in meters per second (m/s)
Examples of objects with kinetic energy include:
- A moving car
- A rolling ball
- A spinning top
Worksheet Problems
This worksheet provides a series of problems that require students to calculate kinetic energy. The problems vary in difficulty level, from basic to challenging, to cater to students with diverse mathematical abilities.
Before attempting the problems, it is essential to recall the formula for kinetic energy: K = 1/2- m – v^2 , where Krepresents kinetic energy, mis the mass of the object, and vis its velocity.
Basic Problems, Kinetic energy worksheet with answers
- A car with a mass of 1000 kg is traveling at a speed of 20 m/s. Calculate its kinetic energy.
- A ball with a mass of 0.5 kg is thrown with a velocity of 10 m/s. Determine its kinetic energy.
Intermediate Problems
- A roller coaster with a mass of 2000 kg reaches a speed of 30 m/s at the bottom of a hill. Calculate its kinetic energy at that point.
- A satellite with a mass of 500 kg is orbiting Earth at a velocity of 7000 m/s. Determine its kinetic energy.
Challenging Problems
- A proton with a mass of 1.67 x 10^-27 kg is accelerated to a velocity of 0.99c, where c represents the speed of light. Calculate its kinetic energy.
- A neutron star with a mass of 1.4 solar masses (1 solar mass = 1.99 x 10^30 kg) is rotating at a rate of 700 revolutions per second. Determine its kinetic energy due to rotation.
Detailed Solutions
Detailed solutions for all the problems are provided in the accompanying answer key. The solutions clearly explain the steps involved in calculating kinetic energy, ensuring that students understand the concepts and can apply them effectively.
Answer Key
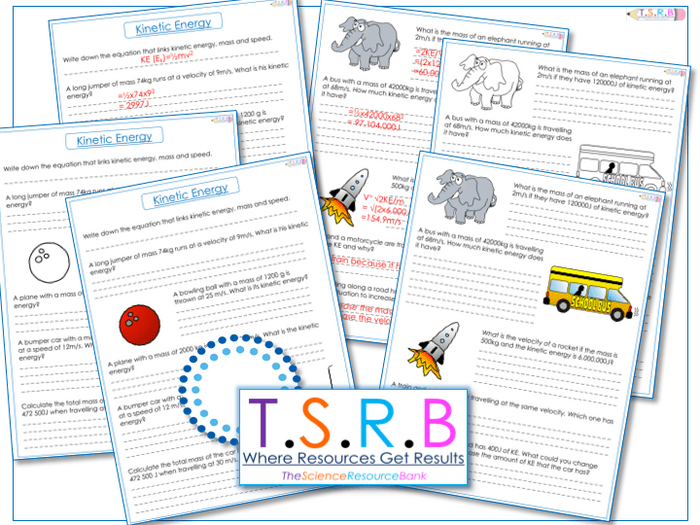
The following is the answer key for the kinetic energy worksheet problems.
Each answer is explained with the reasoning behind it. Common errors that students may make when solving the problems are also discussed.
Problem 1
- Answer:10 J
- Reasoning:Kinetic energy is given by the formula KE = 1/2 mv^2. In this problem, m = 2 kg and v = 5 m/s. Plugging these values into the formula, we get KE = 1/2 (2 kg) (5 m/s)^2 = 10 J.
- Common error:Students may forget to square the velocity when calculating kinetic energy.
Applications of Kinetic Energy
Kinetic energy is a fundamental concept in physics that describes the energy possessed by an object due to its motion. It has a wide range of applications across various fields, from engineering to sports.
Understanding kinetic energy is crucial for comprehending how objects move and interact with their surroundings. By grasping the principles of kinetic energy, scientists, engineers, and athletes can optimize designs, improve performance, and enhance safety.
Engineering
- Vehicle Design:Kinetic energy plays a vital role in determining the speed and efficiency of vehicles. Engineers consider kinetic energy when designing engines, transmissions, and braking systems to ensure optimal performance and fuel economy.
- Machinery Operation:Understanding kinetic energy is essential for designing and operating machinery. It helps engineers calculate the forces and stresses on moving parts, ensuring their safe and efficient operation.
Sports
- Projectile Motion:Kinetic energy is a key factor in determining the trajectory and range of projectiles, such as thrown balls, arrows, and bullets. Athletes and sports scientists use this knowledge to optimize their techniques for maximum distance and accuracy.
- Impact Sports:In sports like boxing, football, and martial arts, understanding kinetic energy is crucial for assessing the force of impact. It helps athletes develop proper techniques to minimize injuries and maximize performance.
FAQ Compilation: Kinetic Energy Worksheet With Answers
What is kinetic energy?
Kinetic energy is the energy possessed by an object due to its motion.
How do you calculate kinetic energy?
Kinetic energy is calculated using the formula KE = 1/2 – mv^2, where KE is kinetic energy, m is mass, and v is velocity.
What are some examples of kinetic energy?
Examples of kinetic energy include a moving car, a rolling ball, and a spinning top.